Numerical Measure of Linear Association Between Two Variables
Measures of association are used in various fields of research but are especially common in the areas of epidemiology and psychology where they frequently are used to quantify relationships between exposures and diseases or behaviours. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient measures the strength of the linear association between variables.
/LinearRelationshipDefinition2-a62b18ef1633418da1127aa7608b87a2.png)
Linear Relationship Definition
Positive relation between two variables.

. Measure of association in statistics any of various factors or coefficients used to quantify a relationship between two or more variables. Statistics and Probability questions and answers. However it is also often used informally as a general measure of how.
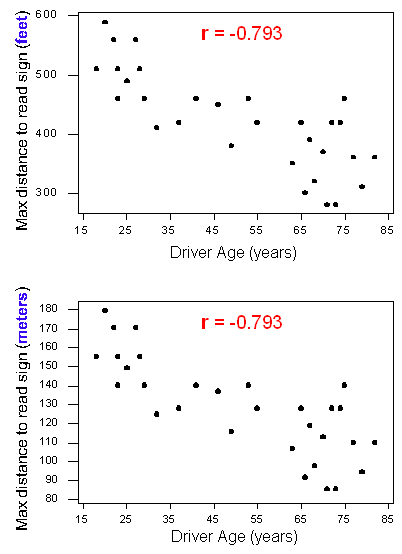
The sign of the Pearson Correlation Coefficient r indicates the direction of the associationslopes up or slopes down A Pearson Correlation Coefficient r with a value near zero implies there is no relationship between the two numerical variables. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the a. Covariance is a measure of how changes in one variable are associated with changes in a second variable.
A numerical value used as a summary measure for a sample such as sample mean is known. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the a. Mean 160 range 60.
To make predictions about the values or y for a given x-value. Who are the experts. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the variance coefficient of variation O correlation coefficient standard deviation.
This R is used significantly in statistics but also in mathematics and science as a measure of the strength of. When writing a regression equation which of. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the.
R developed by Karl Pearson in the early 1900s is a numerical measure that provides a measure of strength and direction of the linear association between the independent variable x and the dependent variable y. A numerical measure such as a mean computed from a population is known as a _____. See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
The correlation-coefficient is a numerical measure of some sort of association amid 2 variables. Coefficient of variation b. The correlation-coefficient is a numerical measure of some sort of association amid 2 variables.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. See the answer See the answer done loading. However the calculation of the correlation r is not the focus of this course.
A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the a. The Correlation Coefficient r.
Standard deviation A Moving to. The correlation coefficient of a sample is most commonly denoted by r and the correlation coefficient of a population is denoted by ρ or R. Positive values of covariance indicate.
A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the _____. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the a. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the Select from AA 1.
Specifically covariance measures the degree to which two variables are linearly associated. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the _____.
Statistics and Probability questions and answers. C To determine if a distribution is unimodal or multimodal. Correlation ranges from negative one to positive one and is used to measure the strength of a linear association between two quantitative variables.
Coefficient of variation c. D Both A and B are correct. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the covariance.
A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the. Coefficient of variation This problem has been solved. QUESITONA numerical measure of linear association between two variables is theANSWERA varianceB covarianceC standard deviationD coefficient of variat.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Mean 160 range 60. A To make predictions about the values of y for a given x-value.
The correlation coefficient r is a numerical measure that measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two quantitative variables. A numerical value used as a summary measure for a sample such as sample mean is known as a a. A correlation closer to negative one indicates a strong negative linear where large values of one variable are associated with small values of the other.
The weights in pounds of a sample of 36 individuals were recorded and the following statistics were calculated. Coefficient of variation c. The correlation coefficient r is a numerical measure that measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two quantitative variables.
None of these answers are correct. A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the _____. Mode 165 variance 324.
B To determine the strength of a linear association between two variables. The weights in pounds of a sample of 36 individuals were recorded and the following statistics were calculated.
Linear Relationships Correlation Biostatistics College Of Public Health And Health Professions University Of Florida

13 2 The Correlation Coefficient Passion Driven Statistics

Nominal Is First Level Of Measurement Nominal Also Known As Categorical Nominal Composed Of Two Mutually Exclusiv Statistics Math Data Science Research Methods
No comments for "Numerical Measure of Linear Association Between Two Variables"
Post a Comment